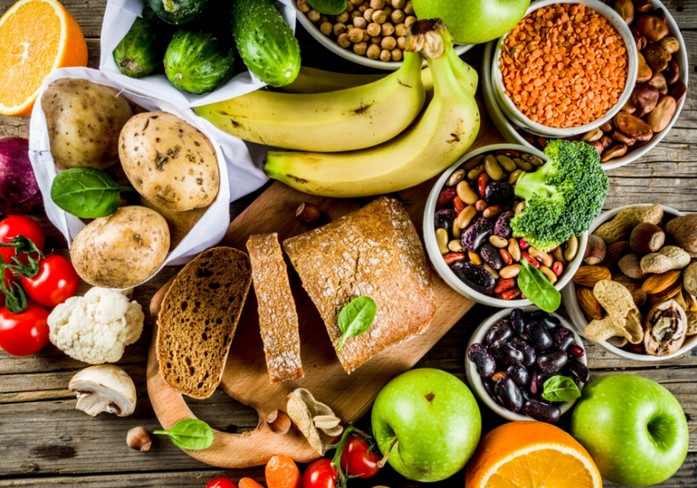

Myths About Carbs continue to shape public opinion about nutrition, often leading people to fear or completely avoid an essential macronutrient. Carbohydrates have been blamed for weight gain, low energy, and even chronic disease, yet they remain one of the body’s primary fuel sources. This widespread confusion is largely the result of oversimplified diet trends and misinformation rather than scientific evidence. Understanding what carbohydrates truly are, how they function, and how different types affect the body is key to making balanced and informed dietary choices.
Carbohydrates Are Not the Enemy
One of the most persistent misconceptions is that all carbohydrates are inherently unhealthy. In reality, carbohydrates are a broad category that includes foods with vastly different nutritional profiles. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes all contain carbohydrates, yet they also provide fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants essential for good health.
The body relies on carbohydrates as its preferred energy source, particularly for the brain and nervous system. When consumed, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which fuels daily activities and supports cognitive function. Eliminating carbohydrates entirely can lead to fatigue, poor concentration, and reduced physical performance. This is why many people experience low energy or irritability when following extremely low-carb diets.
Another common belief is that carbohydrates automatically lead to weight gain. Weight gain occurs when total calorie intake consistently exceeds energy expenditure, regardless of whether those calories come from carbohydrates, fats, or proteins. In fact, carbohydrate-rich foods that are high in fiber tend to be more filling, helping to regulate appetite and support healthy weight management.
Simple vs. Complex Carbohydrates Explained
Not all carbohydrates affect the body in the same way, and understanding this distinction helps clarify much of the confusion surrounding them.
Why Quality Matters More Than Quantity
Simple carbohydrates are typically found in foods like sugary drinks, candy, and refined baked goods. These are quickly digested and can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, followed by energy crashes. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are found in whole grains, beans, and vegetables. They digest more slowly, providing sustained energy and promoting stable blood sugar levels.
The problem arises when all carbohydrates are grouped together without considering their source or structure. Avoiding complex carbohydrates while still consuming refined sugars can actually worsen health outcomes. The key is not to eliminate carbohydrates but to prioritize those that are minimally processed and rich in nutrients.
Fiber is another crucial factor often overlooked in carbohydrate discussions. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot fully digest, yet it plays a major role in digestive health, cholesterol regulation, and blood sugar control. Diets rich in fiber have been linked to lower risks of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain digestive disorders.
Carbs and Metabolic Health
A popular myth suggests that carbohydrates are responsible for metabolic disorders, such as diabetes. While excessive intake of refined carbohydrates and added sugars can contribute to poor metabolic health, carbohydrates themselves are not the root cause. Balanced diets that include whole-food carbohydrate sources have been shown to support metabolic function rather than harm it.
For individuals managing blood sugar concerns, the focus should be on portion control, food quality, and meal timing rather than complete avoidance. Pairing carbohydrates with protein, healthy fats, and fiber can slow glucose absorption and improve blood sugar responses. This approach is far more sustainable than restrictive diets that are difficult to maintain long term.
Carbohydrates also play an important role in physical activity and recovery. During exercise, muscles rely on stored carbohydrates for energy. Adequate carbohydrate intake supports endurance, strength, and post-exercise recovery. Athletes and physically active individuals often experience declines in performance when carbohydrates are excessively restricted.
The Role of Carbs in a Balanced Diet
Another widespread misconception is that carbohydrates have no place in a healthy, modern diet. In truth, many dietary patterns associated with longevity and disease prevention include carbohydrates as a central component. Traditional diets rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables have been linked to lower rates of cardiovascular disease and improved overall health.
Balance is the defining principle. Carbohydrates should complement proteins and fats rather than replace them entirely. When meals are thoughtfully composed, carbohydrates contribute to satiety, energy stability, and nutritional adequacy. Removing them without proper substitutions can lead to nutrient deficiencies and reduced dietary variety.
It is also important to consider cultural and individual differences. Dietary needs vary based on age, activity level, health status, and personal preferences. What works for one person may not be ideal for another, which is why blanket statements about carbohydrates are rarely helpful.
Rethinking Common Diet Trends
Many modern diet trends thrive on the idea that carbohydrates are harmful. While some individuals may benefit from temporary carbohydrate reduction for specific medical reasons, these approaches are often misunderstood and generalized. Long-term health is better supported by moderation and informed choices rather than strict elimination.
Education plays a critical role in dispelling misinformation. When people understand how carbohydrates function and which sources are most beneficial, they are better equipped to make decisions that align with their health goals. Nutrition should empower, not confuse or restrict unnecessarily.
In conclusion, Myths About Carbs have contributed to unnecessary fear and dietary imbalance for many people. Carbohydrates are not inherently harmful; their impact depends on type, quantity, and overall dietary context. By focusing on quality sources, balanced meals, and evidence-based guidance, individuals can move beyond misconceptions and embrace carbohydrates as a valuable part of a healthy lifestyle.





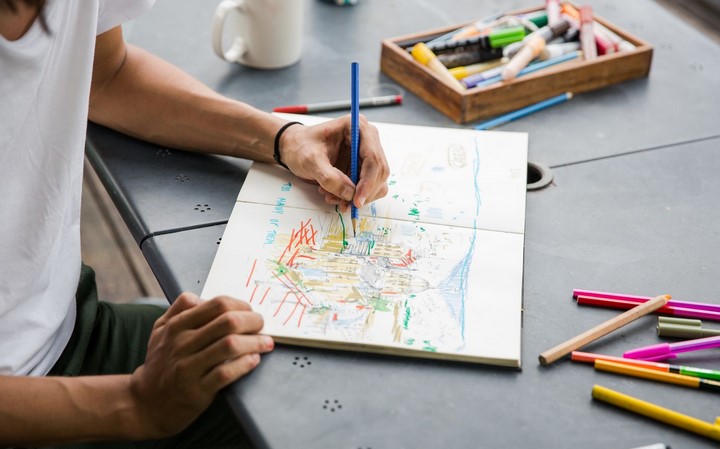 Anxiety has become one of the most prevalent mental health challenges in modern society, affecting individuals across age groups, professions, and cultures. As people search for supportive treatments beyond medication alone, creative and holistic interventions are gaining recognition. Art Therapy for Anxiety has emerged as a valuable approach that uses the creative process to support emotional regulation, self-expression, and psychological healing. Rather than focusing on artistic skill, art therapy emphasizes the process of creating as a means to explore feelings, reduce stress, and foster a sense of control in individuals experiencing anxiety.
Anxiety has become one of the most prevalent mental health challenges in modern society, affecting individuals across age groups, professions, and cultures. As people search for supportive treatments beyond medication alone, creative and holistic interventions are gaining recognition. Art Therapy for Anxiety has emerged as a valuable approach that uses the creative process to support emotional regulation, self-expression, and psychological healing. Rather than focusing on artistic skill, art therapy emphasizes the process of creating as a means to explore feelings, reduce stress, and foster a sense of control in individuals experiencing anxiety.

 Quality sleep is not determined by bedtime alone; it is deeply influenced by the space in which we sleep. A thoughtfully designed bedroom can support the body’s natural rhythms, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. The concept of a Healthy Sleep Environment Setup focuses on aligning your surroundings with your biological and psychological needs for rest. This article introduces the importance of sleep-friendly spaces, explains how environmental factors affect sleep, and provides practical guidance for creating a bedroom that truly supports restorative rest.
Quality sleep is not determined by bedtime alone; it is deeply influenced by the space in which we sleep. A thoughtfully designed bedroom can support the body’s natural rhythms, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. The concept of a Healthy Sleep Environment Setup focuses on aligning your surroundings with your biological and psychological needs for rest. This article introduces the importance of sleep-friendly spaces, explains how environmental factors affect sleep, and provides practical guidance for creating a bedroom that truly supports restorative rest.